Having an understanding of the anatomy of a heart can help you make skilled decisions. When speaking to your cardiologist it’s important to know what their diagnosis is and where that effects your body. If you are dealing with heart failure or cardiovascular disease, here is a breakdown of the anatomy of a heart to help you understand your condition.
Intro To The Anatomy Of A Heart
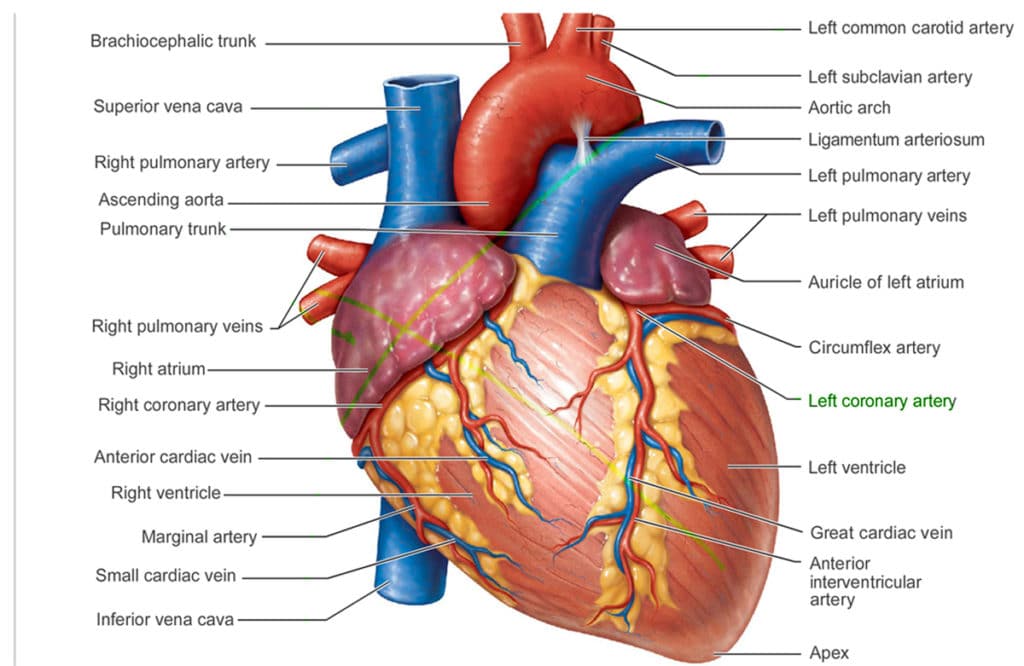 The heart is located between your lungs slightly to the left of your chest behind the sternum. The sternum is the breastbone. Your heart is surrounded by the pericardium which is a membrane like sac to protect your heart. The outermost part of the pericardium surrounds the base of your hearts blood vessels and attached to other parts of your body. This includes the spinal column, diaphragm, and surrounding areas. The innermost part is attached directly to your heart. The layers are separated by a membrane layer that lets your heart beat and move.
The heart is located between your lungs slightly to the left of your chest behind the sternum. The sternum is the breastbone. Your heart is surrounded by the pericardium which is a membrane like sac to protect your heart. The outermost part of the pericardium surrounds the base of your hearts blood vessels and attached to other parts of your body. This includes the spinal column, diaphragm, and surrounding areas. The innermost part is attached directly to your heart. The layers are separated by a membrane layer that lets your heart beat and move.
Every heart has 4 chambers. The two upper chambers are called the atria (left and right). The lower two chambers are your ventricles (left and right). They are separated by the septum which is a very strong muscle. The left ventricle is the strongest and most important chamber of your heart. The walls are only 1/2 inch thick but they are strong enough to pump blood to your whole body.
The Anatomy Of Your Heart Valves
Four valves regulate blood flow through your heart:
- The tricuspid valve manages the blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- The pulmonary valve manages blood flow from the right ventricle into the pulmonary arteries, which run the blood to your lungs get oxygen.
- The mitral valve allows oxygen-rich blood from your lungs move from the left atrium into the left ventricle.
- The aortic valve leads the way for oxygen-rich blood to pass from the left ventricle into the aorta and out into your body.
The Anatomy Of The Conduction System
The conduction system is the electrical system of your heart. The Myocardium, your heart muscle, is contracted by electrical impulses. This begins the SA node that is located at the top of your right atrium. This node is your natural pacemaker and it sets the beat for your heart. The SA node sends an electrical impulse through the muscle fibers of your heart and makes them contract. This makes your heart rate and it can be affected by external factors like stress, physical exercise and hormones.
The Anatomy Of Your Circulatory System
Your heart, veins, and arteries make up the cardiovascular system. The heart pushed the blood to the necessary parts of the body through your circulatory system. Blood provides oxygen and nutrients to every single part of your body through the network of capillaries, arteries, and arterioles. Then blood returns to the heart for more oxygen and nutrients through your veins.
For more information on your heart, visit our educational page at http://centralgaheart.com/educational-videos/heart-anatomy/.