What Is Congestive Heart Failure?
 Congestive Heart Failure is a heart weakness that leads to an excess of fluid in the lungs and
Congestive Heart Failure is a heart weakness that leads to an excess of fluid in the lungs and
other parts of the chest. This build up os often the result of an inability of your heart to pump blood effectively. Conditions, such as narrowed arteries in your heart (coronary artery disease) or high blood pressure, make your heart too weak to work sufficiently. Symptoms can include shortness of breath, fatigue, swollen legs, and rapid heartbeat. This condition generally affects the 40+ age range and can last for many years as a chronic disease. At Central Georgia Heart, our cardiologists often begin assessing congestive heart failure cases through lab work.
What Does Congestive Heart Failure Mean?
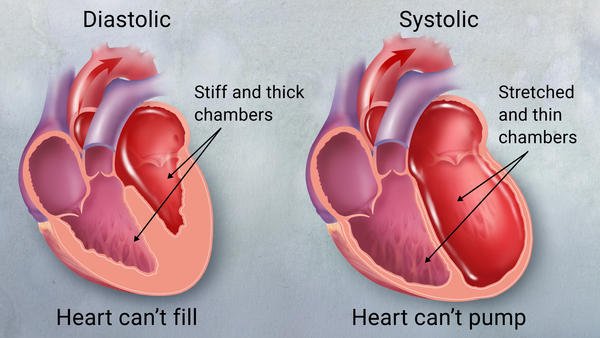
It doesn’t mean that your heart has given up on it’s job. Instead, Heart Failure means that your heart is in a weakened state that makes it move blood at a much slower than normal rate. This creates issues with the tissues surrounding the heart as they tend to stiffen or thicken. Eventually, this condition begins to affect the kidneys causing fluid retention which begins to build up around the arms, legs, ankles, lungs, and more until the body becomes congested.
What Causes Heart Failure?
Congestive heart failure can be caused by a variet of conditions with the heart muscle. The following are a few ways congestive heart failure begins.
- Coronary artery disease is when your artieries cause decreased blood flow to the heart muscle. By preventing blood flow, the arteries experience a lack of oxygen and nutrients.
- Heart attack is when a coronary artery becomes blocked causing damage to the heart muscle resulting in scars that make it function improperly.
- Cardiomyopathy is damage to the heart muscle from causes other than artery or blood flow problems, such as from infections or alcohol or drug abuse.
- Other Conditions like: high blood pressure, thyroid issues, kidney disease,diabetes, or heart defects present at birth can all be triggers of congestive heart failure.